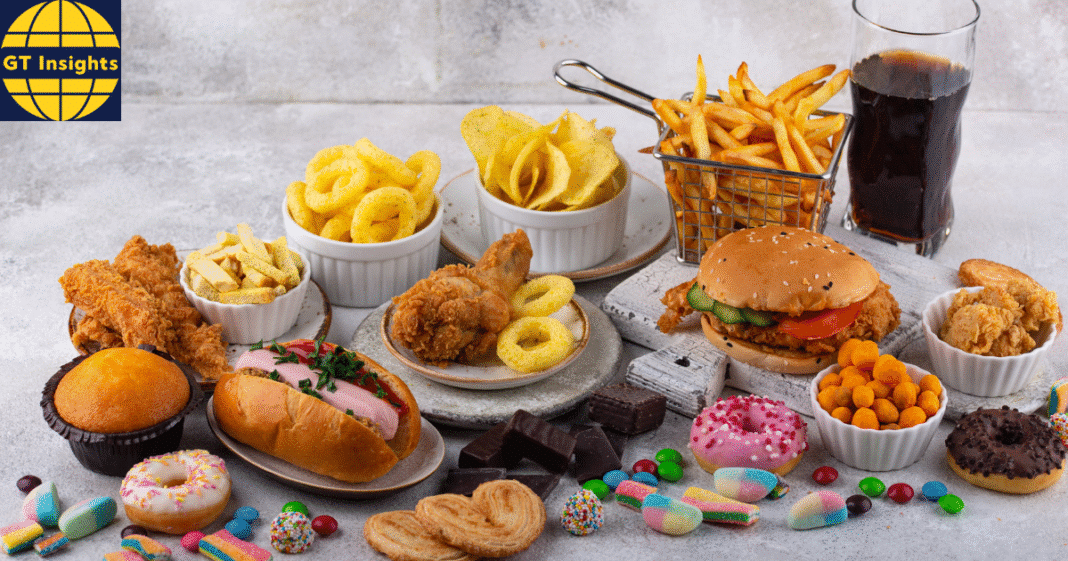With rising concerns surrounding public health, experts are sounding the alarm on ultraprocessed foods. Ultraprocessed Foods health risks are common in these day which are all around us due to our daily eating habits whether its known or unknown. New studies link these convenience-based options to various chronic illnesses. Understanding the health risks of ultraprocessed foods through systems like NOVA and supported by CDC statistics is essential for informed, healthier food choices.
Are Ultraprocessed Foods Making People Sick? Experts Explain the Risks
You know, those rushed family dinners, squeezed in between work, school and bus stops, that rest on anything frozen or boxed. Convenience has become a necessity for so many Americans – but at what cost to our health? Fresh data and new studies are also fueling a growing body of evidence indicating that ultraprocessed foods, a ubiquitous part of modern diets in some countries, may be undermining health in various ways and may help explain rising disease rates and mortality. The consequences are personal, of course, but also reverberate in public policy, economic stability and social equity.
What Are ‘Ultraprocessed’ Foods and Why Do We Need to Avoid Them?
UPFs, or ultraprocessed foods, are factory-formulated products, made using industrial ingredients and additives, with little or no whole or minimally processed foods. Broadly defined, food processing refers to any deliberate change made to a food before it’s consumed, and it includes methods as old as pickling and as recent as artificial sweeteners. Ultr
Identifying Ultraprocessed Food Examples in the Aisle
These (products) are typically formulated with a mixture of processed fats, starches, sugars and protein isolates, with many containing emulsifiers, colorants, flavor enhancers and other additives. That includes processed snacks, sugary cereals, ramen, sweetened yogurt, instant meals, soda, and most store-bought bread products.
The Nutritional Danger of Ultraprocessed Foods
The concern is their nutrition value. If you never hear the term ultraprocessed again, good enough; I doubt I’ll be mentioning it routinely now that it has been lodged in our consciousness, but Hey ! you never know. Plus, they’re loaded with calories and packed in such tiny servings that they give you nothing in return regarding fiber, protein, vitamins, or minerals. The body’s reaction to these ingredients may also explain the explosion in obesity and other chronic conditions in the first world, experts say.
How to Read NOVA Food Classification System
To understand what qualifies as an ultraprocessed food, researchers generally use the NOVA classification system of foods. Developed in 2009 by researchers in Brazil, the NOVA system classifies all foods in four categories:
NOVA Group 1: Fresh or Minimally Processed Foods
Group 1: Fresh or minimally processed foods, including fresh fruits and vegetables, eggs, and milk.
NOVA Group 2: Culinary Ingredients
Group 2: Processed foods such as oils, butter, sugar, and salt.
NOVA Group 3: Processed Foods
Group 3: Processed foods such as cheese, smoked meat, and canned vegetables including added culinary ingredients but not substantially altered.
NOVA Group 4: Ultraprocessed Foods
Group 4 Ultraprocessed: These include practically no whole foods and many added chemical ingredients.
NOVA Food Classification Still Absent in USDA Policy
Despite being endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the NOVA classification has yet to be incorporated officially by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Policy discussions are ongoing about how to best define these foods, particularly when the classification impacts food guidelines and public messaging.
CDC Food Consumption Statistics Show High Reliance on UPFs
Majority of Calories Still From Ultraprocessed Foods
More than half of the calories consumed by U.S. adults between 2021 and 2023 were from ultraprocessed foods. Slightly more than half (53%) of adults’ daily energy intake and a whopping 61.9% of that of individuals under age 19 was provided by UPFs. This is an ever-so-slight improvement over rates from 2017–2018, when adults and children derived 56 and 65.6 percent of their calories, respectively, from such sources, but a collective meh at best.
UPFs Deeply Embedded in Low-Income Life and Food Culture
This information indicates that UPFs continue to be rooted in the American food environment, especially in low-income and high-stress households, in which speed of preparation trumps nutritional consideration.
Also Read, India Floods 2025: 34 Dead in Jammu Landslide, Monsoon Wreaks Havoc
Health Problems Linked to Ultraprocessed Foods
“Problem is, the evidence is very convincing,” he continued, pointing to a large review on the topic published in 2024 in the British Medical Journal that analyzed 45 studies with millions of participants; heavy consumption of ultraprocessed foods was linked to 32 chronic health conditions. These range from the list is by no means exhaustive cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, depression, anxiety disorders, obesity and also elevated all-cause mortality.
Effects of Dietary Displacement
What’s even more alarming about these findings is what the effects of these foods look like. For instance, ultraprocessed foods usually displace healthy meal options, a phenomenon termed “dietary displacement.” Fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins are pushed aside the plate in favor of packaged or microwaveable options.
Processed Food Dangers: Additives Trigger Inflammation and Hormone Disruption
Laced with artificial sweeteners, colors and emulsifiers Many UPFs are added with artificial sweeteners, colorants and emulsifiers. The problem is, these compounds not only light up the brain’s reward pathway – making us want to gorge on more – they also change gut microbes, promote inflammation and can mess up hormone signaling.
Additives in Food Packaging: One More Layer of Risk
One underappreciated danger of ultraprocessed foods is that they are exposed to several different kinds of additives and contaminants. Chemicals directly added to food packaging – such as plastics, paper, glass and metal – include bisphenols, phthalates, perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, and food packaging, as well as coatings, can be sources of this migration. Cumulatively, this results in ongoing biological effects that impact endocrine function and likely elevate cancer risk.
The “Cocktail Effect” of Chemical Exposure
Since these exposures frequently happen simultaneously (termed “cocktail effects”), the health effects may be worse than from an individual chemical. This increased risk highlights the importance of national food safety measures and consumer awareness.
Clinical Data: High-Calorie Diet and Fast Eating Patterns Fuel Obesity
While many of the studies in the BMJ review were based on surveys and observational data, one randomized controlled trial from 2019 was particularly eye-catching. In this trial, 20 healthy adults lived in a medical research facility for one month, and were assigned to two different diets, for two-week periods: ultraprocessed or unprocessed. Following the diets, the UPF diet group consumed an estimated 500 more calories each day and put on an average of two pounds. By comparison, subjects on the unprocessed diet lost two pounds.
Obesity and Ultraprocessed Foods: A Metabolic Disruption
Despite being composed of similar levels of proteins, sugars, fats and sodium, the UPF group poked down more calories and experienced different sensations of subjective satiety. Speed of consumption makes a difference, as faster eating may override the body’s own signals to stop eating and prompt a greater reward response in the brain. In short, UPFs hack the body’s regulatory system, causing irresistable overeating and subsequent long-term weight gain.
Shopping Tips: Identifying Ultraprocessed Foods
Without checking nutrition labels, identifying UPFs by glancing at the products in a typical grocery aisle can be difficult. One reliable way, according to food scientists, is to look at the ingredient list. Foods with five or more ingredients, and ones that include chemical-sounding names – like emulsifiers, color enhancers, high-fructose corn syrup, artificial flavors or hydrolyzed proteins – most probably are classified as ultraprocessed.
The 5-Ingredient Rule of Thumb
One good rule of thumb: If you can’t pronounce or recognize multiple ingredients on the label, consider twice before putting it in your cart.
Processed Food Texture and Chemical Content Are Red Flags
From a reliable point of view, the ingredients that are added just for texture, for preservation or to change the taste, are in fact the main indicator of ultraprocessed food. They are thickeners, anti-foaming agents, bulking ingredients with no nutritional benefit, and they have a huge impact on how your body is going to metabolize it.
Obstacles in Countering Processed Food Threats
It’s not just a matter of personal choice, easy as it may seem to avoid UPF consumption in the abstract. The fight for fair and equitable food is one that involves income inequality, food deserts, educational disparities and Corporate control of the food chain. Healthy food is also clearly more expensive and less available to many Americans, especially those who live in low-income communities.
Economic and Structural Barriers to Healthy Eating
Additionally, many food insecure families depend on government assistance programs or discounted food opportunities – offerings that often include high-calorie, low-nutrient stuff. Without larger systemic changes, asking Americans to get rid of ultraprocessed foods is both impractical and politically tone-deaf.
What Is Being Done and What Can We Do?
Although many government policies promote fruits, vegetables and other foods, bolder moves are required to end reliance on ultraprocessed foods. Among the proposed measures are:
Proposed Measures to Reduce Ultraprocessed Food Dependence
- Initiatives for providing grocery stores that carry fresh fruits and vegetables to food deserts
- Transparent labeling and public information on the health effects of UPFs
- Tighten the regulation of advertising techniques directed at young children
- School nutritional education and public health promotion
Cultural Shift Required Toward Simple, Home-Cooked Meals
However, moving beyond UPFs also involves a cultural shift in the way we think about cooking and time spent in the kitchen. It’s not reasonable to ask everyone to cook every single meal from scratch, but a positive food culture that celebrates good ingredients, older cooking traditions and simple meals could prove a turning point.
Moderation Over Perfection for Lasting Change
Although UPFs can strongly add to obesity and other metabolic disorders, experts warn not to go too much to the other side of the aisle. A little bit of UPF consumption – say, at a birthday party or during a hectic week at work – is not inherently unhealthy. It is the long-term, cumulative intake that constitutes a grave risk to health.
Simple Steps Toward Breaking the UPF Habit
For people hoping to shake their UPF habit, moderation may be a sustainable place to start. Just cooking a few times a week with unprocessed or minimally processed ingredients can nudge the needle toward better health.
Community Changes Lead to Broader Healthy Habits
Social factors are also worth taking into consideration. Healthier behaviors frequently sprout from group settings – via school lunches, workplace wellness programs or community gardening campaigns. Where healthy food starts being a community resource rather than a personal burden, broad change can happen.
Political and Emotional Implications of UPF Consumption
The increasing reliance on ultraprocessed food is not just a health problem, it is deeply emotional and political. The unequal impact of illnesses related to food on low-income communities exposes the failure of food policy and public health. Without dealing with afforbability, education and access – no solution will be enough.
Emotional Toll of Food Insecurity and Decision-Making
Furthermore, the emotional toll of trying to eat healthfully in the face of financial distress can be discouraging. Guilt about feeding one’s family store-brand chicken nuggets instead of organic vegetables deflects attention from larger structural issues that need urgent addressing.
Coda: A Plan For Better Eating
Ultraprocessed foods have embedded themselves in the modern American diet – not only as a matter of convenience, but, for many people, as a necessity. Despite the increasing body of evidence that connects these products with a whole host of health issues, the road to change is complicated. Individual responsibility should intersect with public policy, education and accountability of the food industry.
Conclusion: Moving Forward With Balance and Awareness
The point is not to vilify every packaged snack, or demonize all processed foods. But it’s not all-or-nothing; it’s about slow trajectories, setting our expectations, understanding what’s in our food, and pushing for infrastructures that can make good choices the easy choices. Change must take place at every level – from what’s in our pantries to what’s on Capitol Hill.
FAQs On Ultraprocessed Foods Health Risks
What are the most common health problems linked to ultraprocessed foods?
According to studies, including the recent BMJ study on ultraprocessed foods, heavy UPF consumption is associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular issues, depression, anxiety, and even increased mortality rates.
How can I identify ultraprocessed food examples while shopping?
Check ingredient lists: if a product contains more than five ingredients or unfamiliar names like emulsifiers, colorants, or high-fructose corn syrup, it's likely ultraprocessed. Look for fresh or minimally processed options instead.
Is the NOVA food classification system used in U.S. food policy?
While the NOVA food classification system is recognized by the WHO, the USDA has not yet officially adopted it in U.S. food policy. Discussions on how to categorize and regulate ultraprocessed foods are ongoing.
Can I eat ultraprocessed foods in moderation without health risks?
Occasional consumption of ultraprocessed foods isn’t inherently harmful. The health risks come from long-term, high-volume intake. Prioritizing whole foods and reduced UPF consumption is a healthier long-term strategy.
Reference
New Study Reveals Health Risks of Ultraprocessed Foods